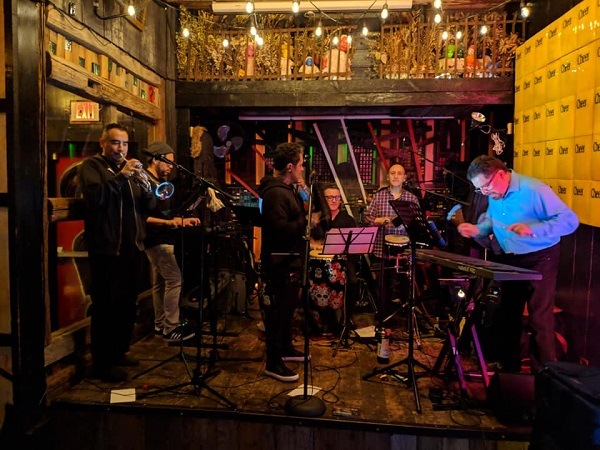
Julio Avila Cuban Band
The Latin music scene in Canada is growing every day thanks to the large number of artists who have decided to move to this beautiful country to try their luck with their talent. Such is the case of Cuban musical director, arranger, composer and singer Julio Avila and the members of his great band Julio Avila Cuban Band.
Given that we thought his career was very interesting, we decided to contact him to learn more about his work and he was kind enough to accept the invitation. Here are the issues we touched on during this fascinating interview.
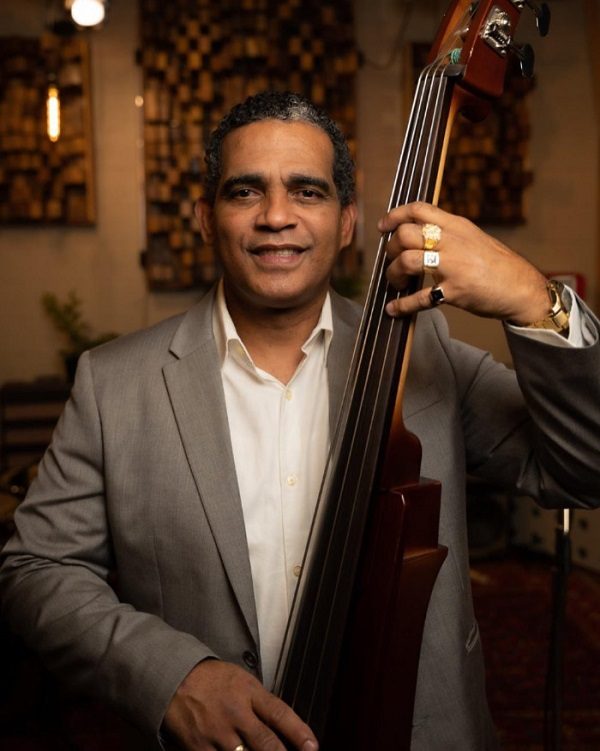

Life for Julio in Guantanamo, Cuba
Contrary to the answer we might expect, Julio told us that making music in Cuba at that time was not difficult, as life was not so expensive and the economic crisis was not as severe as it is now.
In his particular case, things were easier because his mother worked in a radio station and his father was a professional musician and the musical director of the popular music group Por Nuestros Campos for many years until he sadly passed away. It was undeniable that art ran through his veins.
His sister Isabelita was also involved in popular music for many years and was even awarded on several occasions at the local Eduardo Saborit Festival. Today she is retired, but she was very successful locally at the time.
Because all the brothers had a penchant for music, they decided to create a group called Los Hermanos Avila until they all went their separate ways and dedicated themselves to their own professions.
Julio considers that today they would not have been able to devote to this branch of the arts due to the political and economic situation that the island is enduring, and he is thankful that it was not so.
According to his words, the money was enough to buy the instruments in those times, but things become so complicated that developing an artistic career in the Caribbean country is much more difficult.

Changüí
Although he says he has played changüí because of his Guantanamo origins, he was never in a group that based its music on this traditional Cuban dance, as the artist has always liked popular music and salsa.
”Changüí is a genre born in the province of Guantánamo that did not get much popularity, but today, it is impressive the large number of young people who play this dance, since they got a taste for it. In spite of all the years after it was created, there are guys who do not let it die, which makes me very happy” said Julio on this issue.
When we wanted to know why he thinks that these young musicians have opted for this genre and not for other more modern ones such as trap or reggaeton, he replied that the latter two sound a lot in Cuba, but there have been music teachers and schools that have not let changüí die. They continue to teach it to their students and promote it whenever they can.
In addition, there are always groups interested in preserving it in time and uniting it with son and other traditional Cuban genres. They even add flutes and violins, which were not present in the original changüí, in order to give it a unique and modern touch.
Academic background
Julio started playing the guitar being a child of five years old, as he had always seen his parents and older brothers involved in everything that had to do with music. Therefore, it all started in a very natural way and basically on instinct. It was later that both he and his siblings decided to educate themselves in order to become more complete professionals.
In Guantánamo itself, he studied at a music school to become a bassist and began working fully on popular music, which had always been to his liking.
With all that gained knowledge, he decided to move to the city of Havana, to get involved in other projects there and to compose his own material.
Since he was 16, he earned a living as a bassist in a popular music group, which activity he alternated with his secondary education. It can be said that this is the formal beginning of Julio’s musical career.
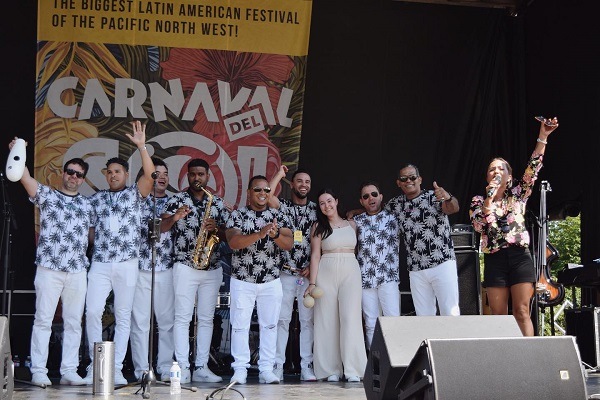

Sonora Universal and Brisas Del Palmar
Before forming his own orchestra, Julio worked with La Sonora Universal and Brisas Del Palmar, which were his first opportunities to shine in the music world.
When the artist was working in a quintet, a trio from the city of Santiago (Brisas Del Palmar) went to a music festival in Guantanamo and thet had the opportunity to meet in a club in 1999. ‘’The musical director of the trio saw us playing and liked the way I played the bass. He told me about the possibility of playing with them, but it did not happen until 2001 when I went to Havana and we met by chance,” Julio said.
After having some time worked with the trio, this musical director met the talented tresista Cesar Echevarría, director of Sonora Universal, who needed a bassist because his stayed in Germany. It was then that he told him about Julio and asked him to see him play, which led them to meet and start working together.
Within a few weeks, Julio was already traveling to Europe with Cesar to tour Germany, Denmark, Holland, Austria and Czechoslovakia. This trip is the one that began to open new doors for him and make him develop as an artist.
Definitive departure from Cuba
When Julio had some time with La Sonora Universal, the director of Brisas Del Mar again asked him to join the group for a tour of Canada in 2005. When he was included, the group went from being a trio to a quartet.
Receptivity from Canadian businessmen was so good that he decided to stay with Brisas Del Palmar permanently until he decided to move from Cuba in 2014 due to the situation which the island was going through.
The latter coincided with the beginning of his love relationship with the Serbian citizen Natasha Marjanovic, who today is his wife, manager of his orchestra and a great life support. It was she who convinced him to stay in Vancouver, a decision he says it was the right one.
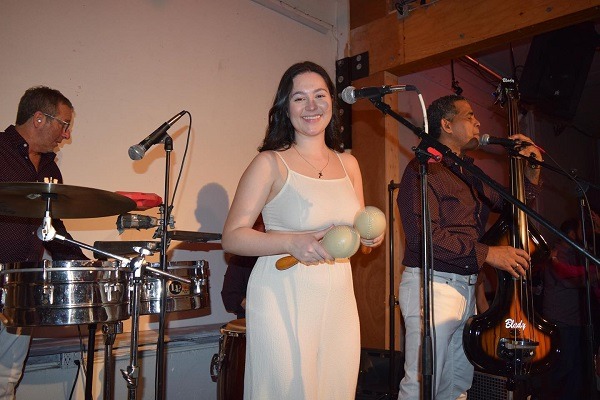

Beginnings of Julio Avila Cuban Band
It all started when Julio needed a pianist for Brisas Del Mar and hired Ernesto Benitez, who, once in Canada, told him that he was not going back to Cuba. That is when he saw the opportunity to start creating his own orchestra from himself and this musician.
The next to be included was percussionist Norman García, with whom Julio and Ernesto formed a trio and began performing at festivals until Isidora Bosanovic, singer and his wife Natasha’s niece, arrived. Her case is very particular because she did not speak Spanish, but she learned it so she could sing in the orchestra. Today, she speaks and sings in Spanish very well.
Finally, the band included Denis Barzaga, another musician originating from Guantánamo, who currently lives in Spain, but when required, travels to Canada to play with the orchestra in Vancouver.
Recently, kettle – drum player Julio Paredes was included to replace Barzaga, who was unable to travel for the time being.
Read also: Puerto Rican singer and talented sonero Charlie Maldonado