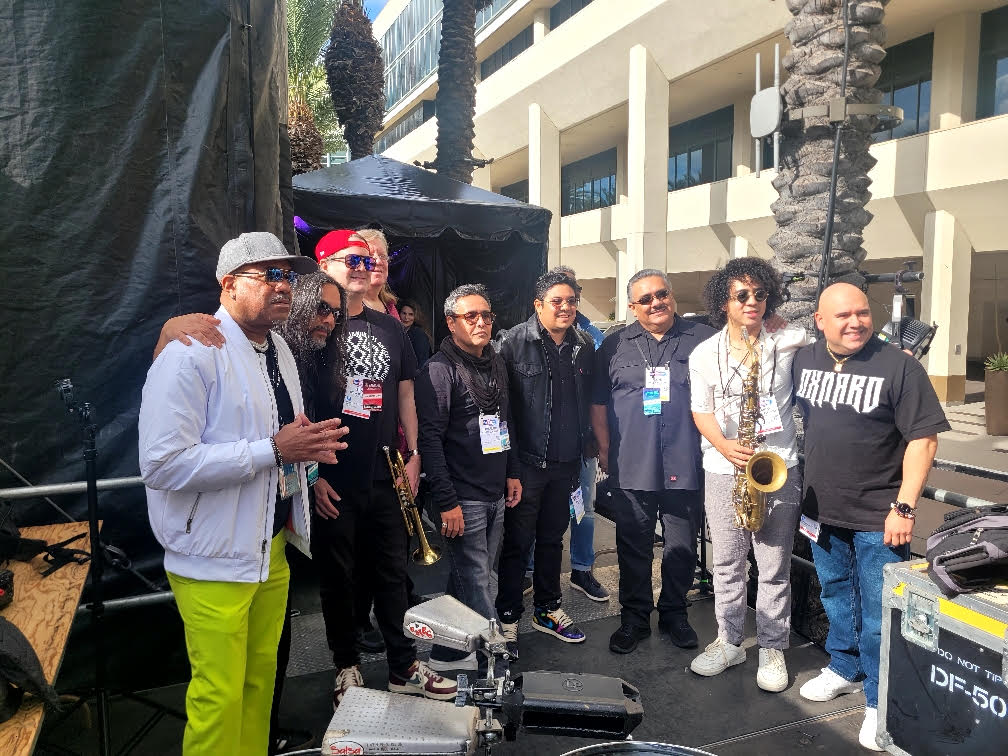
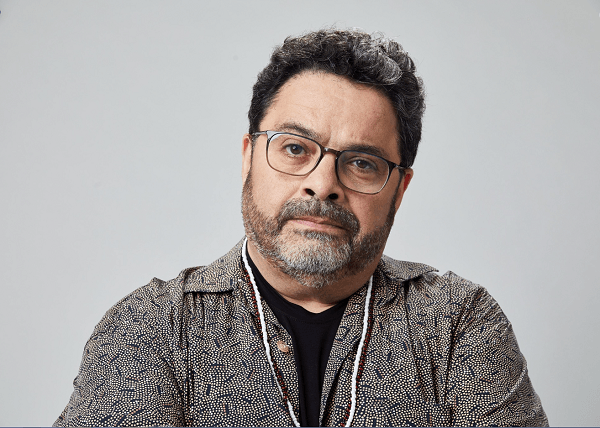
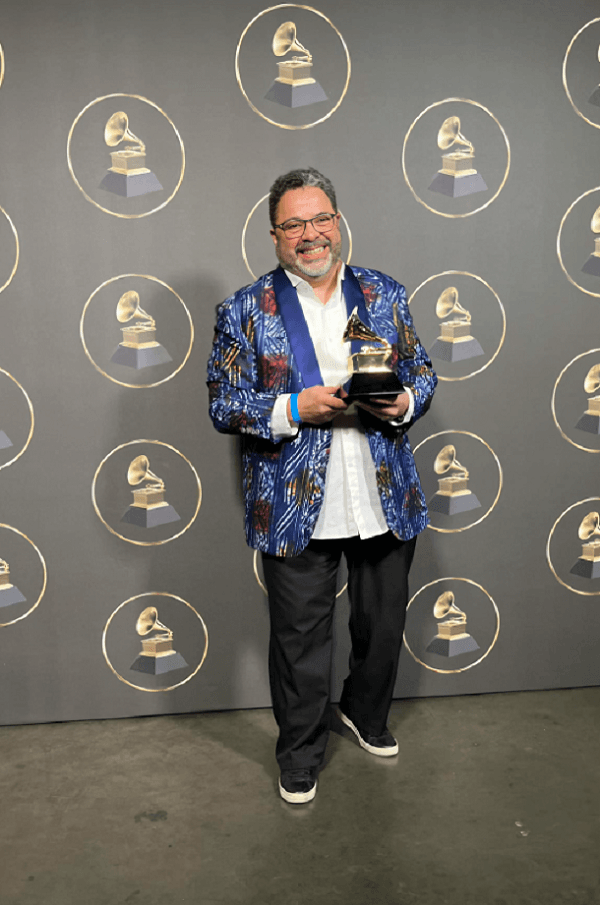
This month’s material is dedicated to the great arranger and trumpeter Ernesto “Tito” Rivera, who year after year has established himself as one of the most respected artists in the Puerto Rican music scene, especially in salsa. Below, we will mention some of the most important facts of his career to date and what he is doing presently.
Important facts of Tito Rivera’s career
One of the greatest contributions the virtuoso Tito has made to music in general has been his pen and the help he has provided to famous orchestras of all time, especially in the 1980s and 1990s. One of these is Roberto Roena y Su Apollo Sound, that to a large extent, is what fans remember today thanks to the Puerto Rican musician’s talented songwriting.
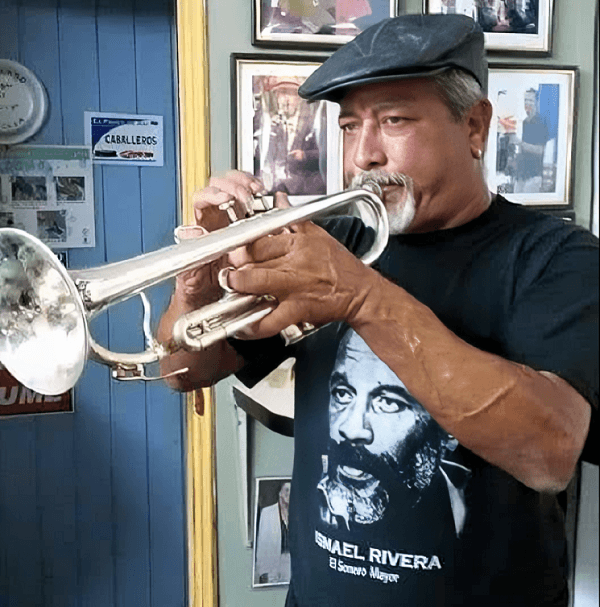

Another orchestra that was strongly influenced by Rivera was La Impacto Crea, which many remember as the group born of Hogares Crea and recorded for Vaya Records under the production of Bobby Valentín. Other groups we can mention on this long list include El Conjunto Borincuba de Justo Betancourt and Tony Yanz Y Su Orquesta Nacimiento.
Similarly, all this talent also gave him the opportunity to collaborate with many big stars, such as Marvin Santiago, who did not doubt to trust the trumpeter who lent his invaluable vision to a number of productions during those years.
And not only that because Tito also left his mark on several songs by Kim De Los Santos Y Su Orquesta, which achieved impressive success in countries such as Colombia and Venezuela.
Caoba y Bambú
Caoba Y Bambú is Tito’s first album as a leader, which represents a major challenge for the sonero’s career. Once again, he demonstrates all the experience he has acquired over decades through the work of other greats who trusted his judgment at the time. Now it is his turn to work on something of his own to which he could apply everything he has learned over the years.
Something very interesting to note about the album is that it brings to life great pieces such as “Musa Y Letra,” which was originally recorded by La Impacto Crea in 1981 for Vaya Records. What changes this time is that the song will be performed by Puerto Rican Jesús “Gumbi” Navedo and Venezuelan Marcial Isturiz. The soneros will also be accompanied by Danny Guzmán’s piano solo.
The fact that “Musa Y Letra” was chosen as the first preview of the album was not a random decision, since it shows that Tito seeks to build an immediate connection with the most classic salsa fans, which only a song as representative as this one can do.
Although this has been a much talked about piece, it is definitely not the only one worthy of mention. We should also talk about “Plaza Vacante,” which is one of El Gran Combo de Puerto Rico’s best-known songs. However, this time, it will be performed by José Luis “Papa Chu” de Jesús, who will, without a doubt, do a magnificent job like the rest of the vocalists.
Another important addition to the album is “Vete Pa’alla,” which was previously recorded by Bobby Valentín for his album “Rompecabezas,” but on this occasion, it will be performed by the talented Davian Raúl.