North America – California – Anaheim
Adelaide Benavides is an artist, a businesswoman and the band leader of Adelaide Tropical.
Born in Texas, Adelaide is based in California with her different projects and putting a lot of creativity and innovation in each one of them.
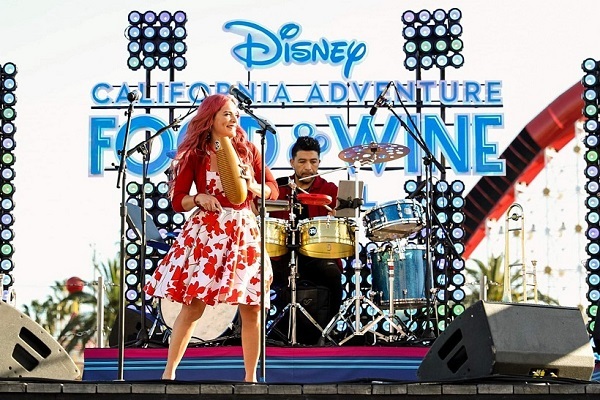

One of the projects that have brought her the most gratifying moments is Adelaide Tropical; a band that has become the official Salsa set of Disney California Adventure.
They are being featured on their largest stage for their Food and Wine Festival. As Adelaide expresses, this band differs from many other Salsa bands because she has achieved bring together a show of which she calls “Salsa Americana“.
Perform classics from Celia Cruz and Tito Puente, but also incorporate a lot of Latin pop that people of all cultures will recognize. Salsa arrangements of popular hits like “Havana”, “Despacito“, Cardi B, Selena and even some original Salsa arrangements of popular Disney songs. This presentation of Salsa has been very successful at Disney and many festivals because of its ability to reach such a wide spanned audience.
Currently, Adelaide Tropical is recording a salsa version and video of “Me voy a enamorar” which will be released this summer. While that moment arrives, you can see Adelaide Tropical perform at Disney California Food and Wine Festival. The Adelaide band is also continuing to perform at Downtown Disney and will be all over the west coast through the end of the summer at various festivals, city concerts, popular venues and every Sunday at Knott’s Berry Farm where they will also be doing a special tribute performance to Selena.
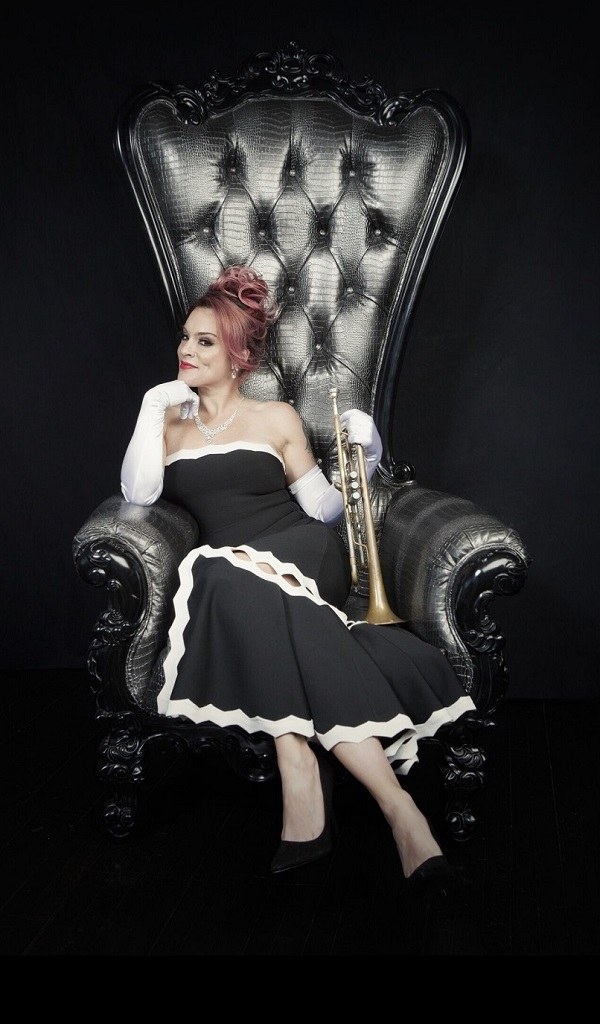

Adelaide Benavides has created different successful formats with great musical quality ando performances that have led her to a variety of venues ranging from Disneyland and Knotts Berry Farm, popular music festivals, grand casinos, and even the Staples Center. She was also a contestant on La Voz México 2018-2019 edition, and recently released her 2nd and all original album “Reflexiones De Mi Mente“, which can be found on all major streaming applications.
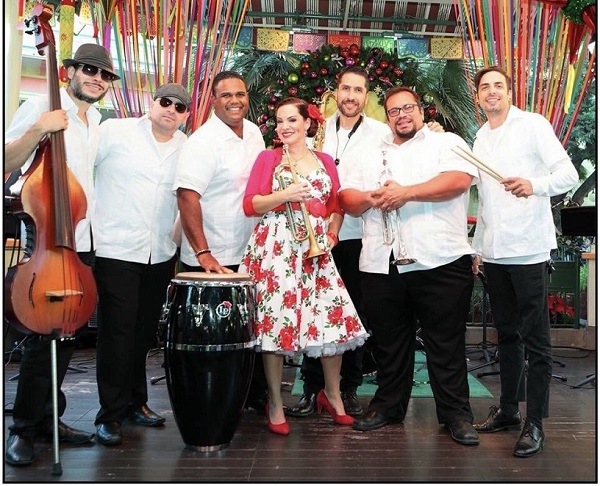

You can also listen the new Adelaide’s album and presentations of Adelaide Tropical on her social media:
Website: Adelaidetheband.com
Email: [email protected]
Instagram: @adelaidepilarmusic
Facebook: Facebook.com/adelaidepilar
Twitter: AdelaidePilar