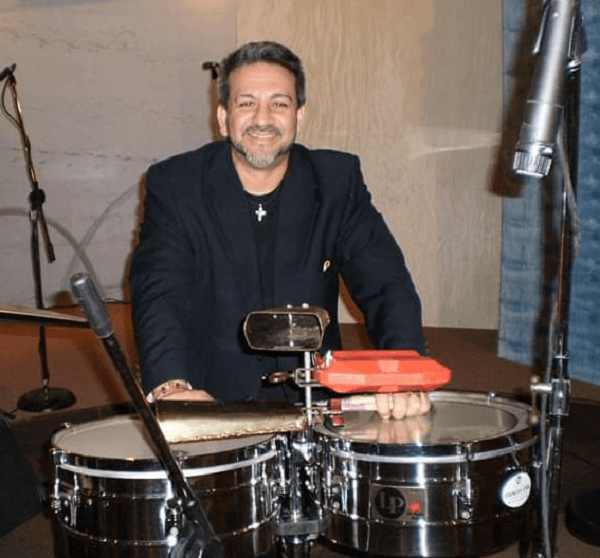
When we talk about the best characteristics of Puerto Rican artists, innovation is definitely one of them, and our guest is an excellent example of this. Grammy nominee and composer William Cepeda was born and raised in Loiza, known as the heart of “Little Africa” in Puerto Rico, so we can sense that this had much to do with his later artistic inclinations. We will talk about this and other things in the next paragraphs of this gripping story.
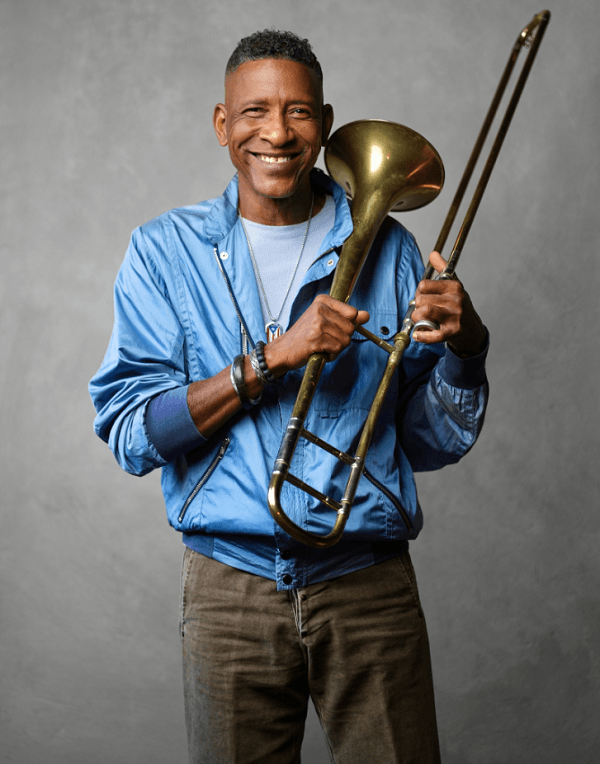
What got William interested in music
The environment in which William grew up had everything to do with his interest in music as a serious profession. In Loiza, Puerto Rican bomba was one of the most listened genres by the community, and cultural events based on it were passed down through generations. It was there that a very young William began attending the colloquially known as “bombazos” and connecting with this music from an early age.
Practically the whole town was involved in these traditions, including his family, so he could not escape all these activities carried out year after year. In fact, his grandparents and some of his uncles and cousins were musicians, so it was common for the young boy to see them play their instruments and know what that was about.
When he turned 14, he finally began seriously studying music, especially the theory part. Although one of his options to study was accounting, this career would never overcome his enormous taste for music, so he never materialized this interest.
How William got started professionally in music
While still an inexperienced teenage musician, William started playing percussion with some local groups, one of them being La Orquesta Zodiac, composed of a group of salsa veterans with more than 50 years of professional experience. Although these gigs were already paid, the young man still saw music as a side hobby.
However, long time later, he would completely change his mind after noticing that his skills and opportunities could take him further than he thought possible.

Afro-Rican Jazz
Having already a more or less consolidated career, William was part of the invention of Afro-Rican Jazz, which can be defined as a concept that celebrates Puerto Rico’s heritage and its African roots while offering a new version of the jazz that everyone knew, giving it a touch of modern flavor that was absolutely innovative for the time.
Growing up in an environment where traditional Puerto Rican music was so present and having experience only with local groups, he still had a long way to go as an artist. His outlook started to broaden by going to study at Berklee in Boston and then to do a master’s degree in New York, which in turn led him to play with American groups and musicians such as Dizzy Gillespie, James Brown, Miriam Makeba, and many other famous jazz musicians.
Gillespie became one of his biggest mentors when playing with him and his group The United Nations Orchestra, which included Cuban, Colombian, Dominican, Panamanian, and Brazilian musicians. It was precisely because of this great diversity of nationalities and influences that the orchestra received this name. However, there were no Puerto Rican musicians or music, so Gillespie gave William the opportunity to become the youngest member and create a subgenre product of a mixture of jazz and some styles from his place of origin.
William told us that many Boricuan musicians used to play Latin jazz based on Cuban music, but none of them had ever ventured to create a subgenre of jazz with a Puerto Rican base. That was when the artist realized that something had to be done about it, so he chose to fuse jazz with Puerto Rican music and later named his group Afro-Rican Jazz.
He also continued to experiment with genres until he found something he called “Plena jazz,” the name he used for one of his albums and the result of mixing plena, another traditional genre born in the neighborhoods of Puerto Rico, and jazz. He also made a symphonic rumba album at the time.
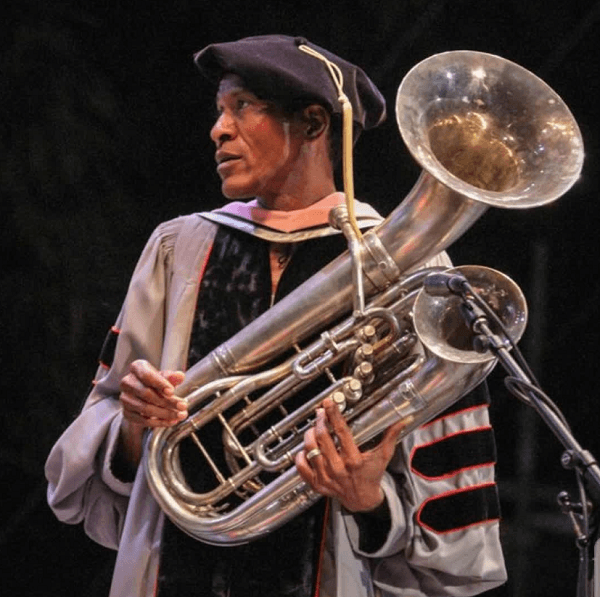

Dizzy Gillespie’s protégé
Although William was influenced by a number of artists, when we check out his story his history, there is no denying that the South Carolinian trumpeter was the greatest influence and role model for the young man.
With respect to this stage of his life, William recalls with affection that Dizzy was always very attentive to his development within the group, to the point that he came to see him as an artistic father. As we said before, he knew nothing about jazz or American music when he left Puerto Rico, but Dizzy and his musicians were “a second university” where he learned what no educational institution could teach him, something he thanks to them.
“Dizzy saw talent in me, so he always pushed me to be better every day. He encouraged me, protected me, and guided me in my development as a musician,” he said of his teacher.
Artists he has collaborated with
William has collaborated with countless great Latin artists such as Celia Cruz, Rubén Blades, Eddie Palmieri, Tito Puente, Marc Anthony, Oscar D’León, and many others. Most of these contacts came about thanks to references of acquaintances, combined with the percussionist becoming known to the public for some time, which generated many recommendations.
All the above artists also influenced him to a certain extent, but he also says that he liked and still likes other genres such as classical music, jazz, the folklore of other countries, and many others.
Read also: Argentine tango bassist and Latin Grammy winner Pedro Giraudo returned to his roots